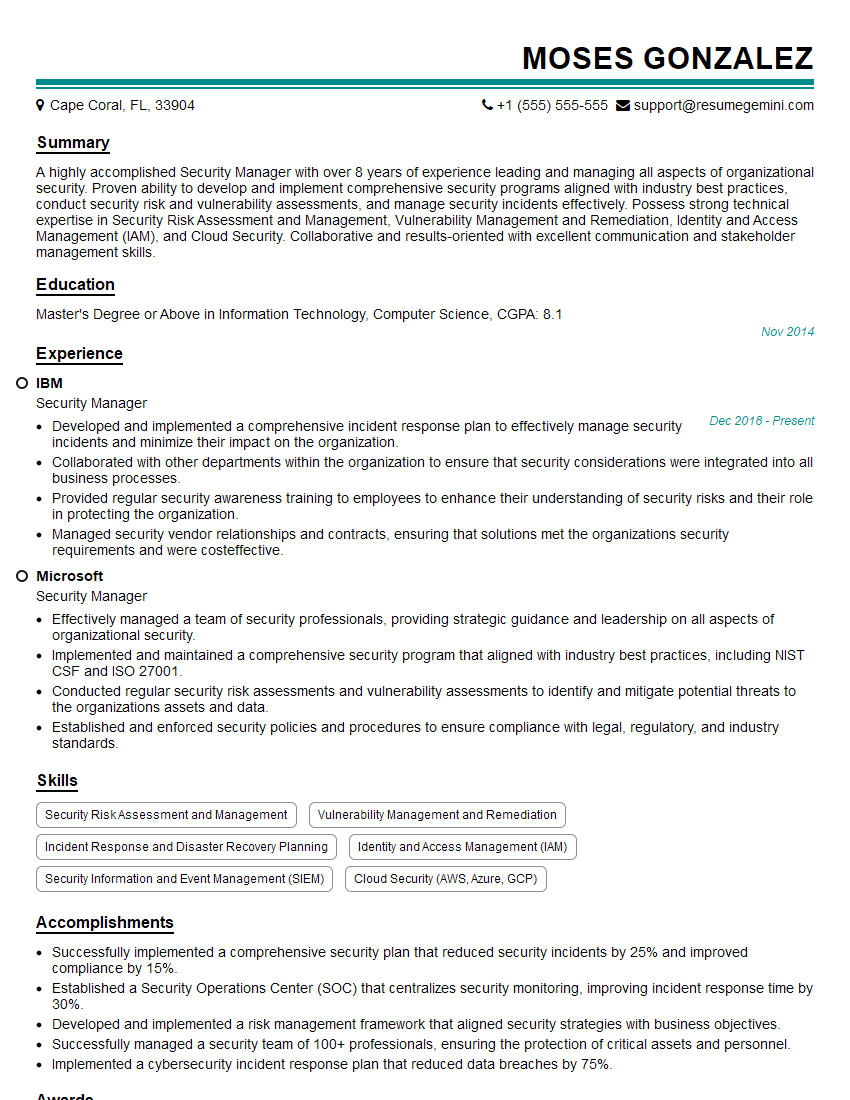
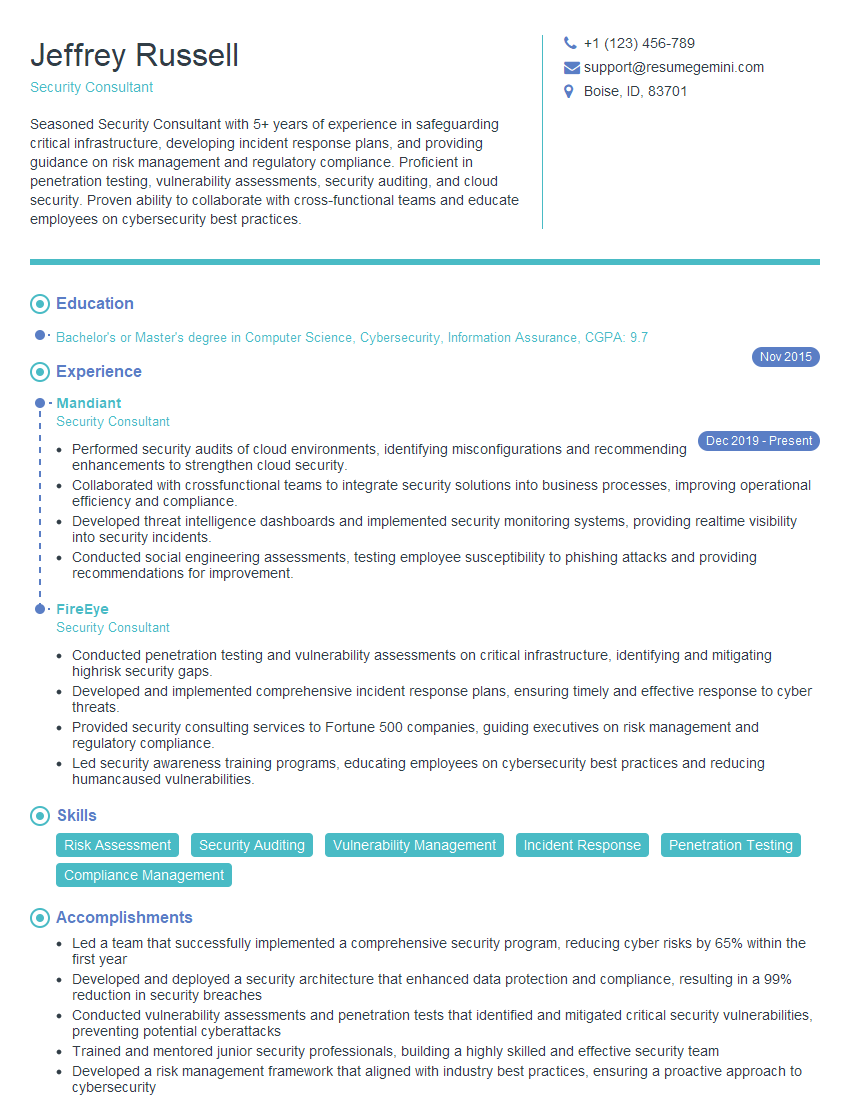
Feeling uncertain about what to expect in your upcoming interview? We’ve got you covered! This blog highlights the most important Counterterrorism and Homeland Security interview questions and provides actionable advice to help you stand out as the ideal candidate. Let’s pave the way for your success.
Questions Asked in Counterterrorism and Homeland Security Interview
Q 1. Describe your understanding of the current global terrorist landscape.
The current global terrorist landscape is incredibly complex and dynamic. We’re seeing a shift away from the large, centrally-organized groups of the past, like Al-Qaeda, towards a more decentralized model. This means a rise in smaller, autonomous cells and lone-wolf actors, often inspired by online propaganda and ideologies, rather than directly controlled by a central command. The rise of online radicalization has enabled this decentralization significantly. Geographically, active terrorist threats remain in regions like the Middle East and Africa, but we also see increasing concerns in other areas due to the ease of global communication and the potential for homegrown extremism. Specific threats evolve, with groups like ISIS and Al-Shabaab continuing to be major players, but new groups and ideologies constantly emerge, adapting to counterterrorism efforts. This fluidity makes predicting and mitigating threats incredibly challenging.
Think of it like a constantly shifting sand dune: you can try to solidify it, but the wind (global events and online radicalization) will always change its shape. Effective counterterrorism requires constant vigilance, adaptation, and robust intelligence gathering.
Q 2. What are the key differences between domestic and international terrorism?
The key difference between domestic and international terrorism lies in the origin and target of the violence. Domestic terrorism involves acts of violence committed within a country’s borders by its own citizens or residents against that same country. The motivation is usually to influence government policy, social change, or intimidate a population within the nation. For example, the Oklahoma City bombing is a prime example of domestic terrorism. International terrorism, on the other hand, transcends national borders. It involves acts of violence committed by individuals or groups from one country against another country or its interests abroad. The goal may be political, ideological, or even religious, but it aims to impact global policy or international relations. Think of the 9/11 attacks; perpetrators were foreign nationals attacking the United States.
While the distinction seems clear, the lines can blur, especially in the age of global interconnectedness. A domestically-based group may receive inspiration or training from international actors, complicating the response. This necessitates strong collaboration between domestic and international law enforcement and intelligence agencies.
Q 3. Explain the concept of asymmetric warfare and its implications for counterterrorism.
Asymmetric warfare describes conflicts where belligerents possess vastly different levels of military strength and technological capabilities. In the context of counterterrorism, it’s a fight between states with sophisticated military apparatus and non-state actors using unconventional tactics such as suicide bombings, hostage-taking, and cyberattacks. Terrorist groups leverage this disparity to their advantage. They avoid direct military confrontation, targeting civilians and soft targets to maximize psychological impact and fear, hoping to achieve their political goals through indirect means.
The implications for counterterrorism are significant. Traditional military approaches are less effective against diffuse, non-state actors. Counterterrorism strategies must adapt to incorporate intelligence gathering, law enforcement, information warfare, and working with international partners to address the underlying political and social conditions that contribute to terrorism.
Imagine a David and Goliath scenario; David (the terrorist group) uses unconventional tactics to overcome Goliath’s (the state) superior strength. This requires a nuanced and multi-faceted response from the state.
Q 4. How effective are current counterterrorism strategies in addressing online radicalization?
Current counterterrorism strategies addressing online radicalization have shown mixed effectiveness. While significant efforts are being made to counter extremist narratives, monitor online activity, and remove or flag extremist content, the sheer volume and speed of information flow online make it a continuous challenge. Furthermore, the use of encryption and the decentralized nature of the internet make it difficult to track and prevent radicalization effectively.
There have been successes in identifying and disrupting online radicalization networks and preventing attacks. However, the cat-and-mouse game between counterterrorism efforts and those seeking to spread extremist ideologies continues. A multifaceted approach including media literacy programs, community engagement, and working with tech companies to flag and remove extremist content is crucial. Success requires a collaborative effort between governments, tech companies, civil society organizations, and individuals.
Q 5. Discuss the role of intelligence gathering in preventing terrorist attacks.
Intelligence gathering plays a crucial role in preventing terrorist attacks. It involves collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information about terrorist groups, their plans, capabilities, and members. This information provides critical insights enabling law enforcement and security agencies to identify potential threats, disrupt planned attacks, and apprehend suspects. Methods include human intelligence (HUMINT), signals intelligence (SIGINT), open-source intelligence (OSINT), and geospatial intelligence (GEOINT).
Think of it as a puzzle; each piece of intelligence, from a phone tap to social media monitoring, contributes to a complete picture of potential threats. Successful intelligence gathering requires collaboration between various agencies, both domestically and internationally, to share and analyze information effectively.
Q 6. What are the ethical considerations in counterterrorism operations?
Ethical considerations in counterterrorism operations are paramount and complex. The inherent tension between national security and individual liberties necessitates careful scrutiny of methods and actions. Key concerns include: the use of torture, targeted killings (including drone strikes), surveillance, data retention and privacy, and the potential for racial profiling and discriminatory practices. The potential for abuse of power and human rights violations is ever-present and requires strict oversight and accountability mechanisms.
Striking a balance between security and ethical conduct requires robust legal frameworks, transparent operational guidelines, and independent oversight bodies to ensure that all actions are lawful, proportionate, and necessary.
Q 7. How can we effectively balance national security with civil liberties?
Balancing national security with civil liberties is a fundamental challenge in the fight against terrorism. It requires a nuanced approach that acknowledges the need for robust security measures while safeguarding fundamental rights and freedoms. This delicate equilibrium demands a strong legal framework defining powers and limitations, robust oversight mechanisms ensuring transparency and accountability, and a commitment to due process and judicial review.
Imagine a scale; national security and civil liberties must be balanced. Overemphasis on one side jeopardizes the other. Effective strategies prioritize proportionate responses, targeted interventions, and a constant re-evaluation of policies and practices to ensure that security measures remain consistent with democratic values and the rule of law.
Q 8. Explain the importance of international cooperation in counterterrorism efforts.
International cooperation is absolutely paramount in counterterrorism. Terrorism, by its very nature, transcends national borders. Terrorist groups often operate across multiple countries, utilizing safe havens, recruiting internationally, and exploiting global vulnerabilities. Therefore, a single nation’s efforts are often insufficient to effectively combat this threat.
- Intelligence Sharing: Countries must share crucial intelligence information regarding terrorist plots, movements, and financing networks. Think of it like a giant puzzle; each country holds a piece, and only by combining them can a complete picture emerge.
- Joint Operations: Collaborative military and law enforcement operations are vital in disrupting terrorist activities, apprehending suspects, and dismantling terrorist organizations. This might involve coordinated raids, joint investigations, or sharing of specialized expertise.
- Legal Cooperation: Extradition treaties and mutual legal assistance agreements are crucial in bringing terrorists to justice. This ensures that individuals involved in terrorist acts are held accountable regardless of their location.
- Combating Financing: International cooperation is essential to tracking and freezing the assets of terrorist organizations, disrupting their financial networks, and preventing the flow of funds across borders. This often requires implementing international sanctions and cooperating on financial intelligence.
- Counter-Narrative Strategies: Joint efforts to counter extremist ideologies and narratives are crucial. This involves sharing best practices, coordinating messaging, and working together to promote tolerance and understanding.
The success of the global war on terror relies heavily on the willingness and ability of nations to collaborate effectively. Examples of successful international cooperation include the dismantling of Al-Qaeda cells through intelligence sharing and the coordinated efforts to disrupt ISIS’s financing networks.
Q 9. Describe the different types of terrorist financing and how they can be disrupted.
Terrorist financing is the lifeblood of terrorist organizations. Disrupting it is crucial to weakening their capabilities. There are several methods:
- Charity Fraud: Terrorists often disguise their funding through legitimate charities, using them as fronts to collect donations that are diverted to terrorist activities. This requires careful scrutiny of charitable organizations and international cooperation to identify and track suspicious transactions.
- Criminal Activities: Groups engage in various criminal activities, including drug trafficking, human smuggling, arms dealing, and kidnapping, to generate revenue. Combating these activities requires international law enforcement cooperation and strengthening border security.
- Hawala Systems: These informal value transfer systems, common in some parts of the world, are often used to move money secretly, making it difficult to trace. Monitoring and regulating these systems, while respecting their cultural context, is vital.
- Online Fundraising: Terrorist groups increasingly rely on online platforms, including social media and cryptocurrency, to raise funds. Tracking these transactions, working with technology companies to identify and remove illicit content, and strengthening cyber security are essential.
- State Sponsorship: In some instances, terrorist groups receive direct or indirect support from state actors, providing them with funding, training, and weapons. Addressing state sponsorship requires diplomatic pressure, sanctions, and targeted actions.
Disrupting terrorist financing involves a multi-faceted approach that includes intelligence gathering, financial investigations, international cooperation, and strengthening regulatory frameworks. It’s like cutting off the head of a hydra – attacking multiple sources simultaneously is crucial to effectively weaken and ultimately dismantle the organizations.
Q 10. How can social media be used to both facilitate and counter terrorism?
Social media is a double-edged sword in the context of terrorism. It can be a powerful tool for both facilitation and counter-terrorism, depending on how it’s used.
- Facilitation: Terrorist groups use social media to recruit members, spread propaganda, radicalize individuals, coordinate attacks, and incite violence. They create online communities, share instructional videos, and disseminate hateful rhetoric, reaching a global audience.
- Counter-Terrorism: Law enforcement and intelligence agencies utilize social media to monitor terrorist activities, identify potential threats, gather intelligence, track suspects, and counter extremist narratives. They can also utilize social media to disseminate accurate information, engage in counter-narratives, and build partnerships with communities vulnerable to radicalization.
Think of it as a battlefield of ideas. On one side, terrorists exploit the anonymity and reach of social media to spread their message. On the other side, authorities and counter-terrorism groups leverage the same tools to identify and neutralize threats and promote resilience. Effective strategies involve close monitoring, proactive content removal, strategic communication, and building partnerships with social media companies.
Q 11. What are some common vulnerabilities exploited by terrorists?
Terrorists exploit various vulnerabilities to achieve their goals. These vulnerabilities can be categorized as:
- Physical Vulnerabilities: This includes poorly secured infrastructure, lax border controls, inadequate surveillance, and lack of physical security measures at critical locations. A simple example is a poorly guarded airport or a vulnerable nuclear power plant.
- Cyber Vulnerabilities: This encompasses weaknesses in computer systems, networks, and data storage, enabling terrorists to steal information, disrupt critical services, or launch cyberattacks. Think of a ransomware attack targeting a hospital or a data breach exposing sensitive information.
- Social and Political Vulnerabilities: These involve societal divisions, political instability, grievances, and a lack of trust in government institutions. Terrorists often exploit these existing tensions to gain support, recruit members, and justify their actions.
- Economic Vulnerabilities: Poverty, unemployment, and economic inequality create fertile ground for recruitment and radicalization. Desperate individuals are more susceptible to extremist ideologies promising solutions and a sense of belonging.
Addressing these vulnerabilities requires a comprehensive approach that combines enhanced security measures, improved infrastructure, bolstering cybersecurity defenses, promoting social cohesion, addressing economic inequalities, and fostering trust in government institutions. It’s a holistic strategy that recognizes the interconnectedness of security threats.
Q 12. Discuss the importance of risk assessment and threat modeling in homeland security.
Risk assessment and threat modeling are fundamental to effective homeland security. They provide a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk Assessment: This involves identifying potential threats, analyzing their likelihood and potential impact, and determining the level of risk. It’s like a systematic evaluation of potential hazards, similar to an insurance company assessing risks before providing coverage.
- Threat Modeling: This focuses on identifying potential attack vectors, analyzing the potential consequences, and developing mitigation strategies. It’s a more targeted approach, visualizing how a threat might exploit vulnerabilities to achieve its objectives.
Both processes inform resource allocation, policy development, and preparedness planning. For instance, a risk assessment might highlight the vulnerability of a specific city to a terrorist attack, leading to increased security measures, emergency preparedness exercises, and investment in infrastructure improvements. Threat modeling might specifically focus on how a particular type of attack, such as a cyberattack on a power grid, could be executed and subsequently develop countermeasures.
Q 13. Explain the role of critical infrastructure protection in national security.
Critical infrastructure protection is crucial for national security. Critical infrastructure encompasses essential services and assets that are vital for the functioning of society. These include:
- Energy: Power grids, oil and gas pipelines, nuclear power plants.
- Transportation: Airports, seaports, railways, highways.
- Communication: Internet, telephone networks, satellite systems.
- Water: Dams, water treatment plants, distribution systems.
- Healthcare: Hospitals, medical facilities.
- Finance: Banks, financial institutions.
Protecting this infrastructure from attacks, whether terrorist acts, natural disasters, or cyberattacks, is vital to maintain essential services, prevent societal collapse, and ensure national stability. This involves physical security measures, cybersecurity enhancements, emergency response planning, and robust regulatory frameworks. Disruption of critical infrastructure can have catastrophic consequences, and therefore, its protection is a top priority for national security.
Q 14. How can we improve cybersecurity to mitigate threats to national security?
Improving cybersecurity is essential to mitigating threats to national security. Cyberattacks can disrupt essential services, steal sensitive information, and undermine national infrastructure. Strategies to improve cybersecurity include:
- Strengthening Network Security: Implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Patching Software Vulnerabilities: Regularly updating software and systems to address known vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation.
- Improving Data Security: Implementing encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention measures to protect sensitive information.
- Enhancing Incident Response Capabilities: Developing plans and procedures to effectively respond to and recover from cyberattacks.
- Investing in Cybersecurity Training and Awareness: Educating personnel about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Working with private sector organizations, international partners, and other government agencies to share information about threats and vulnerabilities.
Cybersecurity is not just a technological issue; it’s a societal challenge requiring a multi-pronged approach involving government, industry, and individuals. It’s a continuous battle against evolving threats, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation.
Q 15. What are some effective strategies for responding to a terrorist attack?
Responding effectively to a terrorist attack requires a multi-faceted approach prioritizing immediate life-saving actions, followed by investigation and longer-term recovery.
- Immediate Response: This phase focuses on securing the scene, providing immediate medical attention to victims (triage is crucial), evacuating survivors, and apprehending any perpetrators. Think of it like a well-orchestrated fire response – quick, decisive action to minimize further harm. First responders need clear communication channels and pre-established protocols to act efficiently.
- Investigation & Evidence Gathering: A thorough forensic investigation is critical. This involves preserving the crime scene, collecting evidence (forensic, digital, witness testimonies), and coordinating with intelligence agencies to identify the perpetrators and their motives. Think CSI, but on a much larger scale, working against a ticking clock to prevent future attacks.
- Recovery & Support: This phase encompasses providing support to victims and their families, repairing infrastructure, and addressing the psychological trauma experienced by the community. It’s about rebuilding trust and resilience in the affected area, perhaps using community outreach programs and mental health support.
For example, the response to the 2005 London bombings involved a rapid coordinated effort across police, ambulance services, and the military, alongside a longer-term strategy to rebuild trust and improve security measures.
Career Expert Tips:
- Ace those interviews! Prepare effectively by reviewing the Top 50 Most Common Interview Questions on ResumeGemini.
- Navigate your job search with confidence! Explore a wide range of Career Tips on ResumeGemini. Learn about common challenges and recommendations to overcome them.
- Craft the perfect resume! Master the Art of Resume Writing with ResumeGemini’s guide. Showcase your unique qualifications and achievements effectively.
- Don’t miss out on holiday savings! Build your dream resume with ResumeGemini’s ATS optimized templates.
Q 16. Describe the importance of collaboration between different government agencies in homeland security.
Collaboration between government agencies is the bedrock of effective homeland security. No single agency possesses all the necessary resources, expertise, or intelligence to tackle the complex threat of terrorism effectively.
- Information Sharing: Agencies like the FBI, CIA, DHS, and local law enforcement need to share information seamlessly to identify patterns, disrupt plots, and respond to incidents. This requires overcoming bureaucratic hurdles and fostering a culture of trust and transparency.
- Joint Operations: Successful counterterrorism requires joint operations, especially in scenarios like large-scale emergencies or high-risk investigations. This involves coordinating resources, personnel, and strategies across different agencies.
- Resource Pooling: Pooling resources – financial, technological, and human – allows for more effective use of limited funds and better leverage of specialized skills. For example, the Coast Guard can collaborate with Customs and Border Protection to secure maritime borders.
The failure to collaborate effectively, as exemplified by some criticisms of intelligence failures leading up to 9/11, highlights the critical need for inter-agency coordination.
Q 17. How can we improve information sharing among law enforcement and intelligence agencies?
Improving information sharing requires addressing both technological and cultural challenges.
- Technology: Implementing secure, interoperable data systems is crucial. This includes creating standardized data formats and encryption protocols, allowing agencies to exchange information efficiently and safely. Imagine a secure digital platform accessible only to authorized personnel, with tools for efficient search and analysis.
- Legal Framework: Clear legal frameworks and guidelines are necessary to regulate information sharing while protecting privacy rights. This involves balancing national security concerns with individual liberties.
- Cultural Shift: Fostering a culture of trust and transparency is paramount. Agencies need to break down bureaucratic silos and create incentives for information sharing, possibly via rewards for intelligence sharing and repercussions for its absence.
One example of improvement is the creation of fusion centers, which bring together law enforcement and intelligence agencies at the state and local levels to share information and analyze threats. However, challenges remain in balancing speed and accuracy with the need to ensure the privacy and security of data.
Q 18. Discuss the role of community engagement in preventing terrorism.
Community engagement is a crucial, often overlooked, component of terrorism prevention. It relies on building relationships and fostering trust between law enforcement and the communities they serve.
- Building Trust: Community policing strategies and outreach programs can build trust and create opportunities for information sharing. This includes regular meetings, community events, and accessible communication channels.
- Early Warning Systems: Engaging with communities allows for the identification of potential threats early on, before they escalate. Community members might notice suspicious activities or individuals that law enforcement might otherwise miss.
- Counter-Narratives: Community engagement helps to counter extremist narratives and promote social cohesion. This may include educational programs, interfaith dialogues, and initiatives that celebrate diversity.
For instance, programs that encourage community members to report suspicious activity anonymously have proven effective. A strong community partnership can significantly improve the prevention of acts of terrorism.
Q 19. How effective are current border security measures in preventing terrorist entry?
Current border security measures are effective to a degree, but they are not foolproof. The sheer volume of legitimate travel and the constant evolution of terrorist tactics present significant challenges.
- Technological Advancements: Improved technologies such as advanced screening systems, biometric identification, and data analytics improve detection capabilities. However, terrorists continuously adapt their methods, making technology a constant arms race.
- Human Element: Despite technological advancements, the human element remains crucial. Dedicated, well-trained border agents are essential to identify suspicious individuals and cargo. This needs consistent training, and sufficient staffing.
- Vulnerabilities: Border security faces challenges such as porous land borders, vast coastlines, and the potential for exploitation of legal entry points. This requires a holistic approach, involving multiple agencies and intelligence sharing.
While significant progress has been made in enhancing border security since 9/11, the persistent threat necessitates continuous evaluation and adaptation of strategies.
Q 20. Explain the challenges in detecting and disrupting improvised explosive devices (IEDs).
Detecting and disrupting IEDs presents considerable challenges due to their inherent variability and the ease of construction.
- Improvisation: IEDs can be made from readily available materials, making them difficult to predict or detect using standard methods. This requires a wide range of detection equipment, customized to different environments.
- Concealment: IEDs can be hidden almost anywhere, making detection difficult and potentially dangerous. This includes the use of sophisticated techniques to mask the presence of explosives.
- Technological Advancement: Terrorist groups often adapt their methods to circumvent existing detection technologies, requiring continuous investment in research and development of new detection tools and techniques.
This is a cat-and-mouse game: While technology can help, human intelligence and skilled bomb disposal experts remain crucial to mitigating the threat of IEDs. Advanced training programs for bomb technicians, including virtual reality simulations, are key to improving capabilities.
Q 21. What are the key components of a comprehensive emergency response plan?
A comprehensive emergency response plan (ERP) is a crucial element of preparedness. It outlines procedures to manage emergencies efficiently, minimizing casualties and damage.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities is the first step. This involves understanding the specific risks faced by a community, organization, or nation.
- Mitigation Strategies: Developing strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of emergencies is crucial. This includes preventive measures and risk reduction initiatives.
- Preparedness Measures: Stockpiling resources, training personnel, and establishing communication protocols are essential elements of preparedness. This involves regular drills and simulations.
- Response Plan: The plan should detail actions to be taken during an emergency, including establishing command structures and coordinating emergency services. This could include detailed flowcharts and checklists for different scenarios.
- Recovery Plan: Procedures for post-emergency recovery are essential, including rebuilding infrastructure, providing support to victims, and learning from the incident.
A well-crafted ERP should be regularly reviewed and updated, adapting to changing threats and lessons learned from previous incidents. Think of it as a living document, constantly evolving to improve preparedness.
Q 22. Discuss the psychological impact of terrorism on individuals and communities.
Terrorism’s psychological impact is devastating and far-reaching, affecting individuals and communities profoundly. It goes beyond the immediate physical damage; the trauma extends to mental health, social structures, and the overall sense of security.
Individuals: Victims directly involved experience PTSD, anxiety, depression, and grief. Even those who weren’t physically harmed can develop these conditions due to witnessing violence, experiencing loss of loved ones, or living under the constant threat of attack. This can lead to long-term challenges like sleep disorders, social isolation, and difficulty functioning in daily life.
Communities: Entire communities can suffer from collective trauma. Trust erodes, social cohesion weakens, and fear becomes pervasive. Businesses may suffer economic hardship, leading to job losses and further strain on resources. The feeling of vulnerability and insecurity can lead to social unrest and increased polarization.
Example: The 9/11 attacks caused widespread PTSD, not just among those directly affected but also among first responders, rescue workers, and even individuals who witnessed the events on television. The sense of insecurity affected air travel and national policies for years to come.
Addressing the psychological impact requires a multi-faceted approach, including mental health services, community support programs, and initiatives to promote resilience and social healing. It’s crucial to recognize that the recovery process is long and complex, requiring ongoing support and understanding.
Q 23. Describe your experience with threat analysis and risk assessment tools.
My experience encompasses a wide range of threat analysis and risk assessment tools, both quantitative and qualitative. I’ve used tools like STRIDE (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, Elevation of Privilege) for software security analysis and more comprehensive frameworks like the National Infrastructure Protection Plan (NIPP) for broader critical infrastructure assessments.
Quantitative Tools: These involve statistical modeling and data analysis to identify patterns and predict potential threats. This includes using algorithms to analyze large datasets of information related to past attacks, social media activity, or financial transactions to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Qualitative Tools: These involve expert judgment and subjective evaluation. This includes conducting interviews with intelligence sources, analyzing open-source information, and utilizing scenario planning to anticipate potential future threats and challenges.
Example: In one assessment of a large public event, I used a combination of quantitative data (crowd size projections, historical incident rates) and qualitative factors (potential protest groups, weather conditions) to assess the risk of potential disruptions and develop a comprehensive security plan.
The key is to combine these approaches for a holistic understanding. A purely quantitative approach can miss crucial contextual details, while a purely qualitative one can be subjective and lack rigor. A balanced approach, supported by rigorous methodologies, is essential for effective threat assessment.
Q 24. How would you approach evaluating the credibility of an intelligence source?
Evaluating the credibility of an intelligence source is paramount. It’s a multi-step process that relies on careful analysis and triangulation of information.
Source Background Check: First, I’d investigate the source’s past behavior, motivations, and potential biases. Have they provided reliable information in the past? What are their potential connections to the subject of interest? Are there any incentives for them to provide false or misleading information?
Information Corroboration: Information from a single source should never be taken at face value. I’d verify the information with other independent sources and analyze for consistency. Discrepancies warrant deeper investigation.
Method of Information Gathering: How did the source obtain the information? Was it firsthand knowledge, hearsay, or inference? This influences the weight and reliability of the information provided.
Contextual Analysis: The information’s context is crucial. Does it fit within a broader pattern of activity? Does it align with known intelligence or open-source information?
Example: If a source claims imminent terrorist attack, we’d verify this against other intelligence reports, analyze the source’s past accuracy, and consider any potential motives for deception. If the claim lacks corroboration from multiple independent sources, its credibility is significantly reduced.
Q 25. Describe your experience working within a multi-agency team.
I’ve extensive experience working in multi-agency teams, which are crucial in counterterrorism and homeland security. Successful collaboration requires clear communication, mutual respect, and a shared understanding of goals and responsibilities.
Communication Protocols: We employ standardized communication protocols, including secure platforms and regular briefings, to ensure seamless information sharing among agencies. This avoids duplication of effort and promotes efficient response.
Role Clarification: Each agency has specific expertise and responsibilities. A clear delineation of roles and responsibilities prevents conflicts and ensures that everyone focuses on their area of expertise.
Joint Exercises & Training: Regular joint exercises and training sessions help to build rapport and develop effective coordination mechanisms between different agencies, enhancing our ability to respond to real-world threats.
Example: In one operation involving a potential cyber threat, our team comprised representatives from law enforcement, intelligence agencies, and cybersecurity firms. Effective communication and clear role definition allowed us to swiftly contain the threat and prevent significant damage.
Q 26. How do you stay current with developments in the field of counterterrorism and homeland security?
Staying current is critical in this rapidly evolving field. I employ a multi-pronged approach to ensure my knowledge remains up-to-date.
Professional Journals & Publications: I regularly read leading journals and publications focusing on counterterrorism and homeland security, such as Studies in Conflict & Terrorism and the Journal of Homeland Security and Emergency Management.
Conferences & Workshops: Attending conferences and workshops allows for interaction with other experts, exposure to cutting-edge research, and networking opportunities.
Online Resources & Databases: I utilize online resources and databases such as government websites, think tank reports, and academic databases to access the latest research and information.
Professional Networks: Maintaining a network of contacts within the field provides access to insights and information not readily available through public channels.
Continuous learning is not merely an option; it’s a necessity. The landscape of threats is constantly shifting, requiring ongoing adaptation and refinement of our understanding and strategies.
Q 27. What are your thoughts on the effectiveness of current counter-terrorism legislation?
Current counter-terrorism legislation is a complex issue with both successes and shortcomings. While some legislation has been effective in disrupting terrorist plots and enhancing national security, other aspects raise concerns regarding civil liberties and potential for abuse.
Effectiveness: Legislation targeting financing of terrorism, strengthening intelligence gathering capabilities, and improving information sharing has proven beneficial in preventing attacks. However, the effectiveness varies depending on the specific legislation and its implementation.
Concerns: Some critics argue that certain laws unduly infringe on civil liberties, particularly regarding surveillance and data retention. The balance between national security and individual rights remains a delicate and ongoing debate.
Challenges: Adapting legislation to the evolving tactics of terrorist groups is a constant challenge. Terrorist organizations often use innovative methods to evade detection and exploit legal loopholes.
A balanced approach is essential – one that prioritizes national security while upholding fundamental rights and freedoms. Regular review and updates to legislation are crucial to ensure its effectiveness and adaptability to the ever-changing threat landscape.
Q 28. Describe a time you had to make a critical decision under pressure in a security-related situation.
During a large-scale public event, a credible threat emerged late in the planning stages. We had a short window to assess the situation and implement mitigation strategies before the event commenced.
Assessment: Our team rapidly analyzed the threat, considering its credibility, potential impact, and feasibility of mitigation. We weighed the risks of canceling the event against the risks of proceeding with heightened security.
Decision: We decided to proceed with the event but implemented significant changes to the security plan. This included increasing police presence, deploying additional security personnel, implementing enhanced screening procedures, and deploying counter-drone technology.
Outcome: The event proceeded without incident. The swift decision-making and implementation of the revised security plan were pivotal in ensuring public safety. Post-event analysis highlighted the importance of contingency planning and proactive communication.
This situation underscored the need for clear protocols, decisive leadership, and the ability to adapt under pressure. The collaborative spirit within the team was critical to our success.
Key Topics to Learn for Counterterrorism and Homeland Security Interview
- Threat Assessment and Analysis: Understanding various terrorist methodologies, identifying potential threats, and evaluating risk levels. Practical application includes analyzing intelligence reports and developing preventative strategies.
- Intelligence Gathering and Analysis: Methods for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence relevant to counterterrorism efforts. Practical application includes interpreting data from various sources and identifying patterns indicative of terrorist activity.
- Cybersecurity and Critical Infrastructure Protection: Recognizing vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure and developing strategies to mitigate cyber threats against national security. Practical application includes understanding cybersecurity protocols and incident response procedures.
- Homeland Security Policy and Legislation: Familiarity with relevant laws, regulations, and policies governing homeland security operations. Practical application includes understanding the legal framework within which counterterrorism activities are conducted.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Developing and implementing plans for responding to terrorist attacks or other national emergencies. Practical application includes understanding crisis management techniques and coordinating responses across multiple agencies.
- International Counterterrorism Cooperation: Understanding the importance of international collaboration in combating terrorism. Practical application includes familiarity with international treaties and agreements related to counterterrorism.
- Radicalization and De-radicalization: Understanding the processes of radicalization and developing strategies for de-radicalization. Practical application includes recognizing warning signs and developing intervention strategies.
Next Steps
Mastering Counterterrorism and Homeland Security opens doors to impactful and rewarding careers, contributing significantly to national security. To stand out, creating a compelling and ATS-friendly resume is crucial. This ensures your qualifications are effectively highlighted to potential employers. ResumeGemini is a trusted resource to help you build a professional and impactful resume, tailored to your specific experience and career goals. We provide examples of resumes specifically tailored to Counterterrorism and Homeland Security roles to help you showcase your skills and experience effectively. Take the next step towards your dream career; craft a resume that reflects your expertise and dedication.
Explore more articles
Users Rating of Our Blogs
Share Your Experience
We value your feedback! Please rate our content and share your thoughts (optional).
What Readers Say About Our Blog
Interesting Article, I liked the depth of knowledge you’ve shared.
Helpful, thanks for sharing.
Hi, I represent a social media marketing agency and liked your blog
Hi, I represent an SEO company that specialises in getting you AI citations and higher rankings on Google. I’d like to offer you a 100% free SEO audit for your website. Would you be interested?